News
-
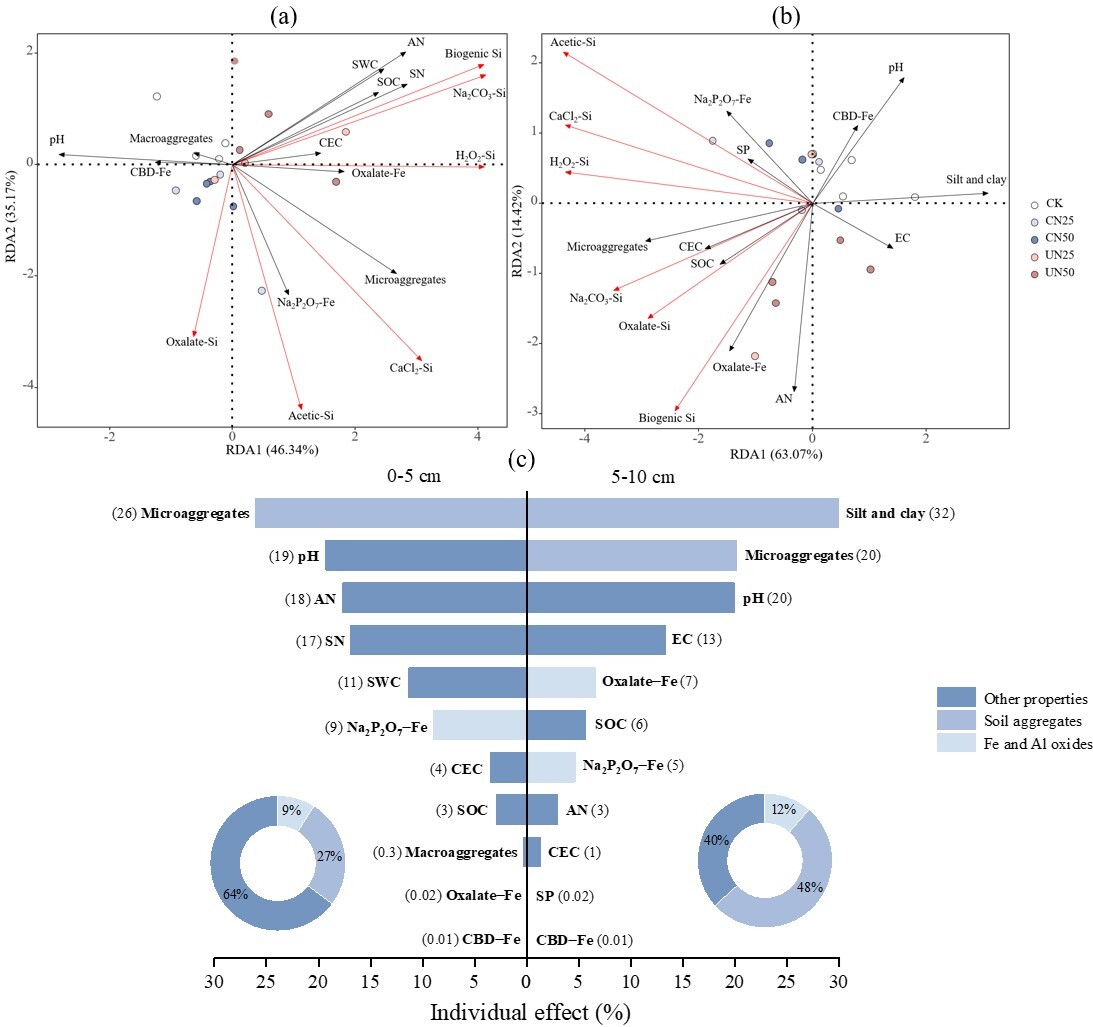
2026-03-09Contrasting responses of soil silicon forms to different nitrogen−addition approachesInvestigating the impacts of chronic atmospheric nitrogen (N) deposition on soil silicon (Si) forms is critical for predicting terrestrial Si biogeochemistry, but the influence of N deposition on soil Si forms in subtropical forests is vague.Here, Yu et al. (2026) evaluated the impacts of 12 year’s canopy and understory N−addition on soil Si f... Atmospheric N deposition caused by human activities has dramatically affected terrestrial ecosystem Si cycling, especially in tropical and subtropical forests. Soil Si dynamics play important roles in plant growth and defense and are tightly linked to silicates weathering processes, with direct consequences on carbon dioxide (CO2) consumption. M...Read More
-
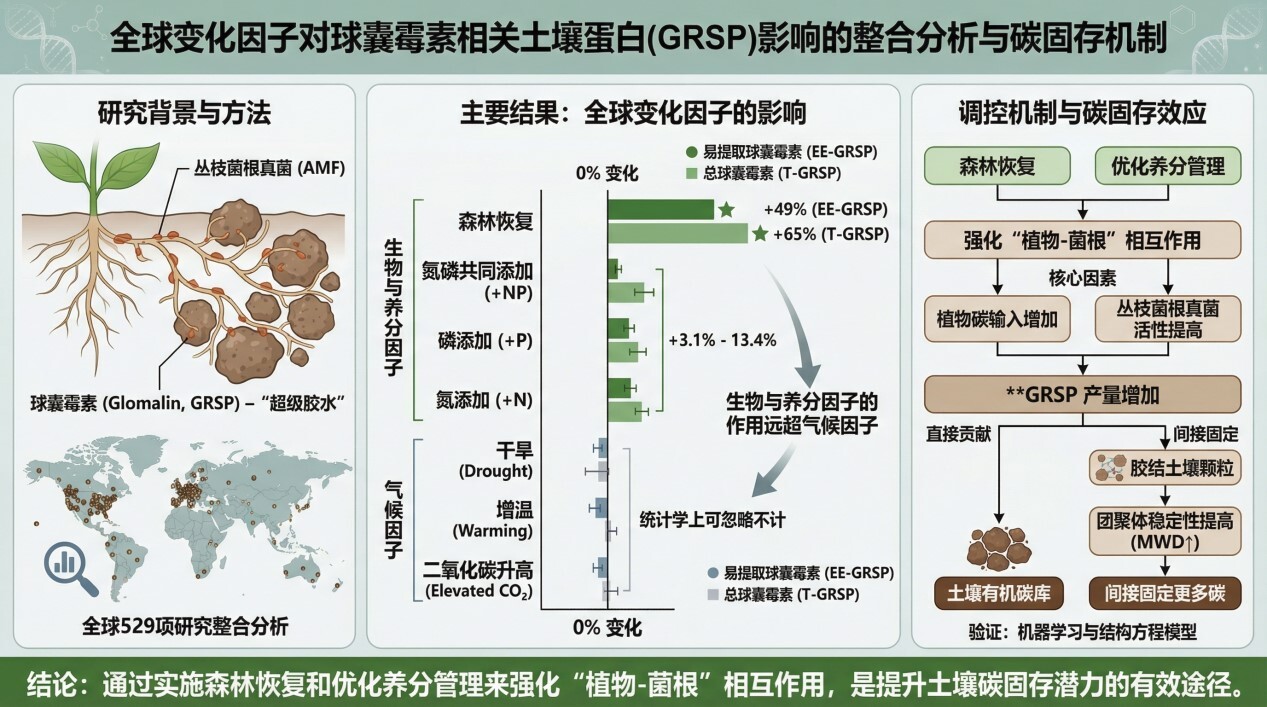
2026-03-09Global change reshapes glomalin-mediated soil carbon sequestration by influencing plant inputsThrough a meta-analysis of 529 observations from 122 studies worldwide, we found that nitrogen and phosphorus additions, their co-application, and forest restoration significantly increased both easily extractable and total glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) by alleviating nutrient limitations and stimulating plant inputs and arbuscular mycorr... Glomalin-related soil proteins (GRSP), key metabolites secreted by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), are renowned as the "super glue" maintaining soil organic carbon (SOC) stability. However, under the backdrop of global climate change, the dynamic responses of this critical protein have not yet been quantified on a global scale.Based on a met...Read More
-
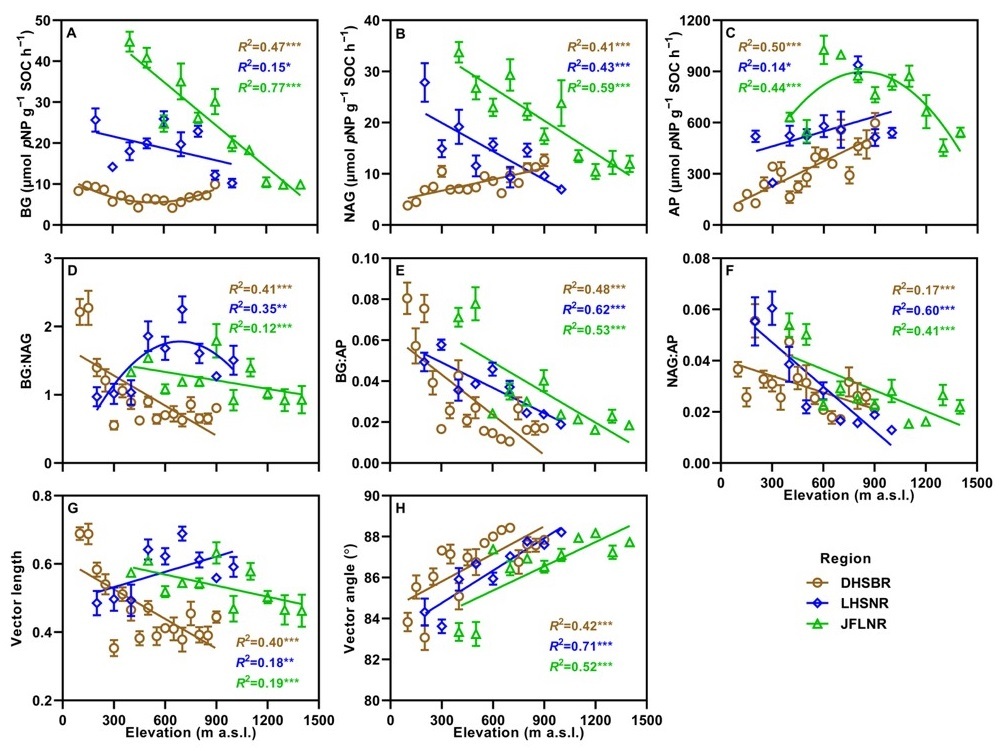
2026-02-14Elevation Aggravates Phosphorus Limitation of Soil Microorganisms in Tropical ForestsAcross tropical forest elevational gradients, soil microorganisms exhibit pervasive phosphorus limitation that intensifies with increasing elevation. Lower temperatures at higher elevations constrain phosphorus release while enhancing microbial investment in P-acquiring enzymes, with important implications for soil carbon cycling under climate c... Researchers from the Ecology and Environmental Science Center of the South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with international partners, have demonstrated that soil microorganisms in tropical forests are widely constrained by phosphorus (P) availability, and that this limitation becomes significantly stronger...Read More
-
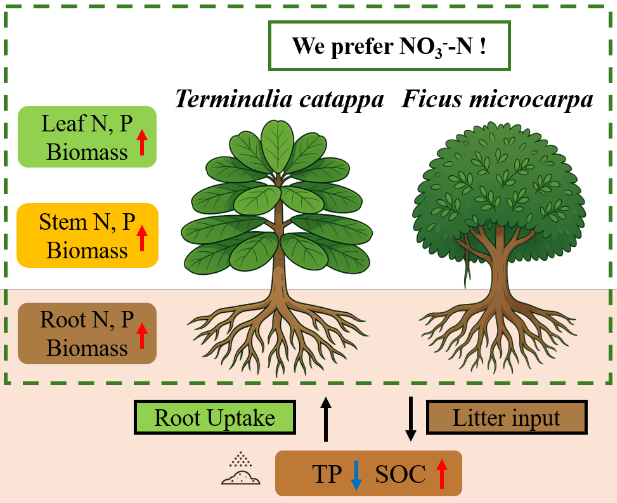
2026-02-08Significant Progress in Nitrogen Form Regulation for Soil Nutrients and Vegetation Restoration on Tropical Coral IslandsThe form of nitrogen fertilizer significantly impacts its efficacy, yet the optimal form for tropical coral islands remains unclear. This study found that nitrate-nitrogen provides greater benefits to both the soil properties and plant growth on these islands. Tropical coral island soils suffer from high alkalinity and poor nutrient holding capacity, making nitrogen a critically limiting factor for plant life. While traditional restoration efforts often involve heavy fertilizer use, this approach risks severe nitrogen loss and environmental damage. Recently, a team from the Xiaoliang Research Station ...Read More
-
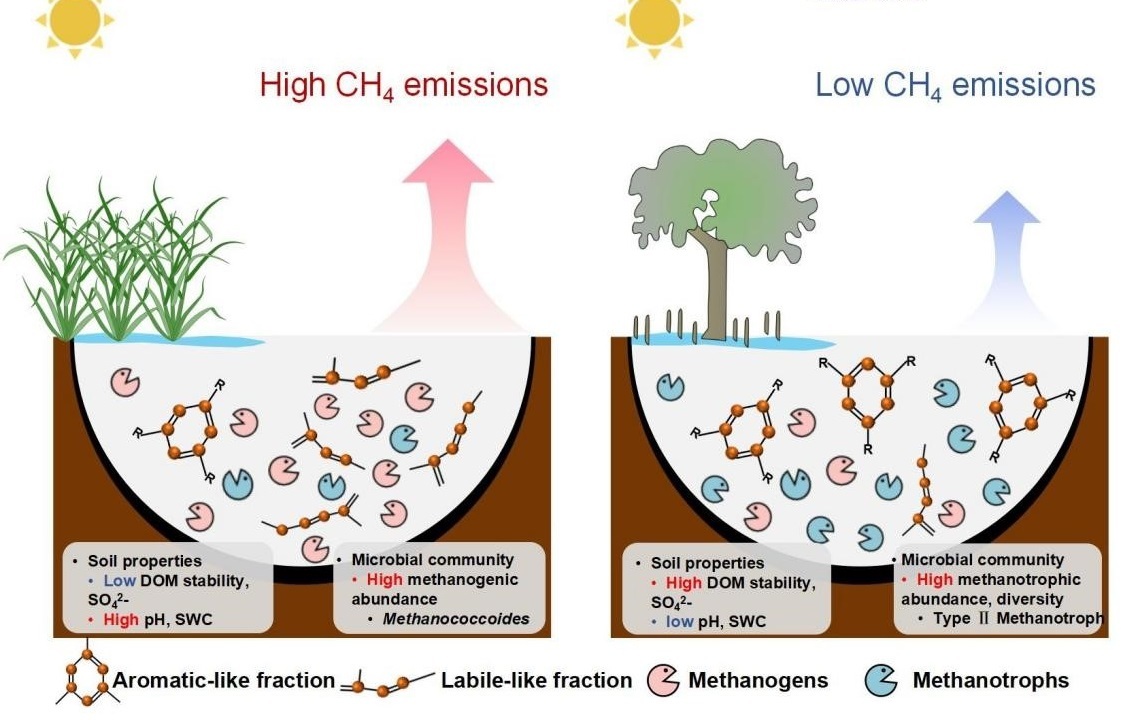
2026-02-08The Microbial Mechanisms by Which Spartina alterniflora Invasion Weakens Carbon Sequestration in Coastal WetlandsSpartina alterniflora has rapidly expanded in China’s coastal wetlands, but its effects on methane emissions remain unclear. Using one-year in situ monitoring and integrated biogeochemical and microbial analyses, this study shows that Spartina invasion increases soil methane emissions by enhancing labile organic matter and altering methane-cycl... Spartina alterniflora is one of the most rapidly expanding invasive plant species in China’s coastal wetlands over recent decades. Owing to its fast growth rate and substantial organic matter inputs, this species has the potential to profoundly alter soil carbon cycling processes. However, whether and how S. alterniflora invasion modifies metha...Read More
-
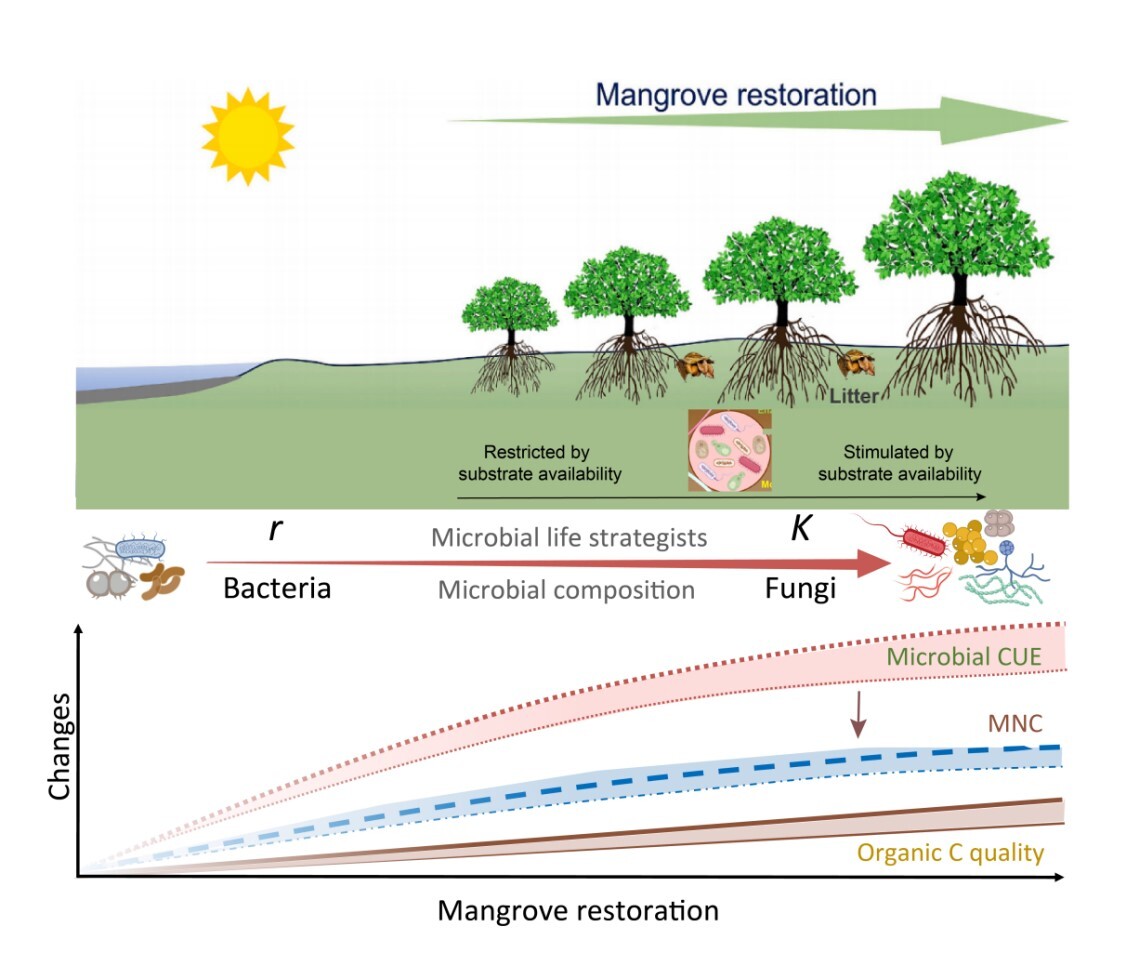
2026-01-29Scientific Breakthrough in Blue Carbon: Mangrove Restoration Enhances Soil Carbon Sequestration via Microbial PathwaysMangrove restoration significantly enhances microbial carbon use efficiency and promotes microbial necromass carbon accumulation by improving organic carbon quality and driving a shift in microbial community from r-strategists to K-strategists. These findings highlight the importance of incorporating microbial processes into restoration strategi... A recent study led by researchers (Prof. WANG Faming, Dr. HUANG Xingyun, and so on) at the Xiaoliang Experimental Station has shed new light on the crucial role of soil microbes in carbon sequestration during mangrove restoration, providing a novel microbial-driven perspective for enhancing "Blue Carbon" sinks.Published in the Journal of Plant E...Read More
-
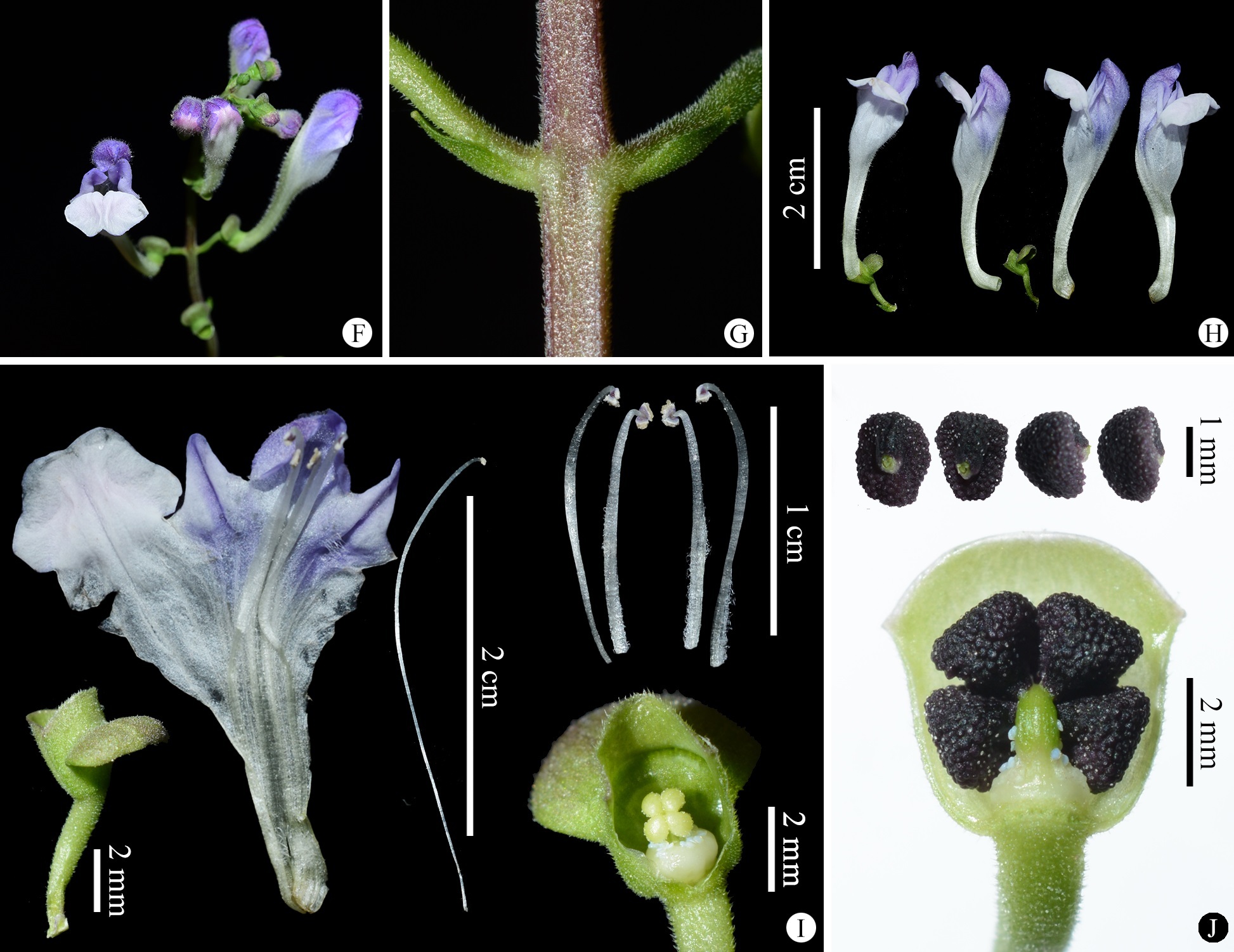
2026-01-29Unraveling the Taxonomic History of Scutellaria formosana: A Hundred-Year QuestBased on critical examination of original description and herbarium specimens and careful observations of living plants in the wild, we demonstrated that the type locality of Scutellaria formosana of Lamiaceae (also known as the mint family) previously regarded as a native of Taiwan or Hainan provinces, China, is actually Hong Kong, and S. formo... In 1894, a flowering Scutellaria plant from the Veitch & Sons nursery was described by the British botanist N. E. Brown as a new species, Scutellaria formosana Brown (Fig. 1). It was characterized by having glabrous stems, ovate leaves nearly obtuse at the apex, broadly cuneate at the base, inconspicuously toothed at the margin, and glabrous on ...Read More
-
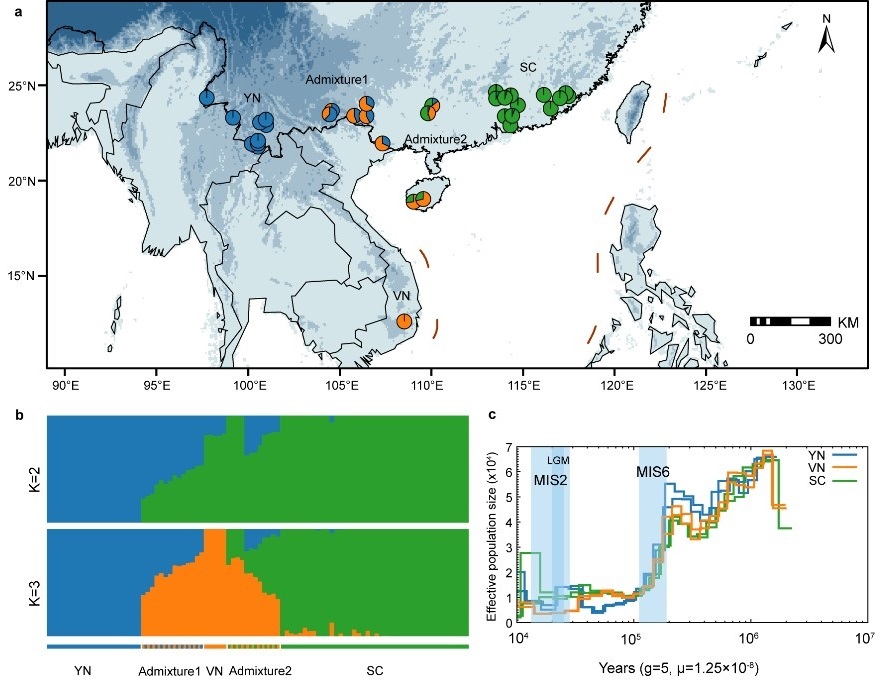
2026-01-20Decoding the Genome of Brainea insignis Reveals Insights into Fern Evolution and ConservationFerns are an ancient lineage of vascular plants, yet limited genomic resources constrain both evolutionary and conservation inference. Here, we generate a chromosome-level genome assembly for the endangered cycad fern Brainea insignis (8.62 Gb), the sole species in its genus within eupolypods II, and integrate comparative and population genomic... The persistence of rare plant species is not only a matter of individual species survival but also underpins the maintenance of ecosystem functions and the continuity of long evolutionary histories. For monotypic genera, population decline or extinction entails the erosion or complete loss of entire evolutionary lineages, resulting in irreversib...Read More