News
-
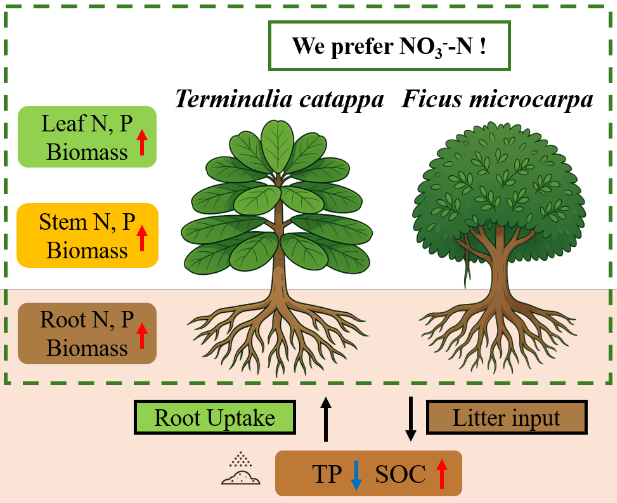
2026-02-08Significant Progress in Nitrogen Form Regulation for Soil Nutrients and Vegetation Restoration on Tropical Coral IslandsThe form of nitrogen fertilizer significantly impacts its efficacy, yet the optimal form for tropical coral islands remains unclear. This study found that nitrate-nitrogen provides greater benefits to both the soil properties and plant growth on these islands. Tropical coral island soils suffer from high alkalinity and poor nutrient holding capacity, making nitrogen a critically limiting factor for plant life. While traditional restoration efforts often involve heavy fertilizer use, this approach risks severe nitrogen loss and environmental damage. Recently, a team from the Xiaoliang Research Station ...Read More
-
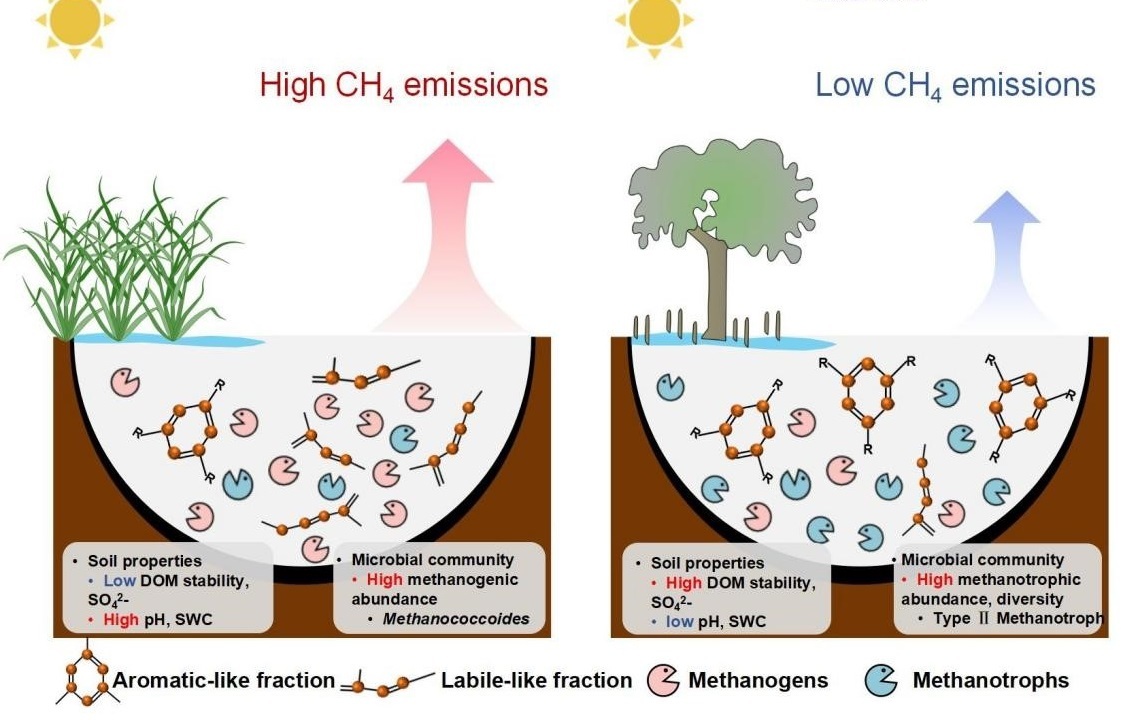
2026-02-08The Microbial Mechanisms by Which Spartina alterniflora Invasion Weakens Carbon Sequestration in Coastal WetlandsSpartina alterniflora has rapidly expanded in China’s coastal wetlands, but its effects on methane emissions remain unclear. Using one-year in situ monitoring and integrated biogeochemical and microbial analyses, this study shows that Spartina invasion increases soil methane emissions by enhancing labile organic matter and altering methane-cycl... Spartina alterniflora is one of the most rapidly expanding invasive plant species in China’s coastal wetlands over recent decades. Owing to its fast growth rate and substantial organic matter inputs, this species has the potential to profoundly alter soil carbon cycling processes. However, whether and how S. alterniflora invasion modifies metha...Read More
-
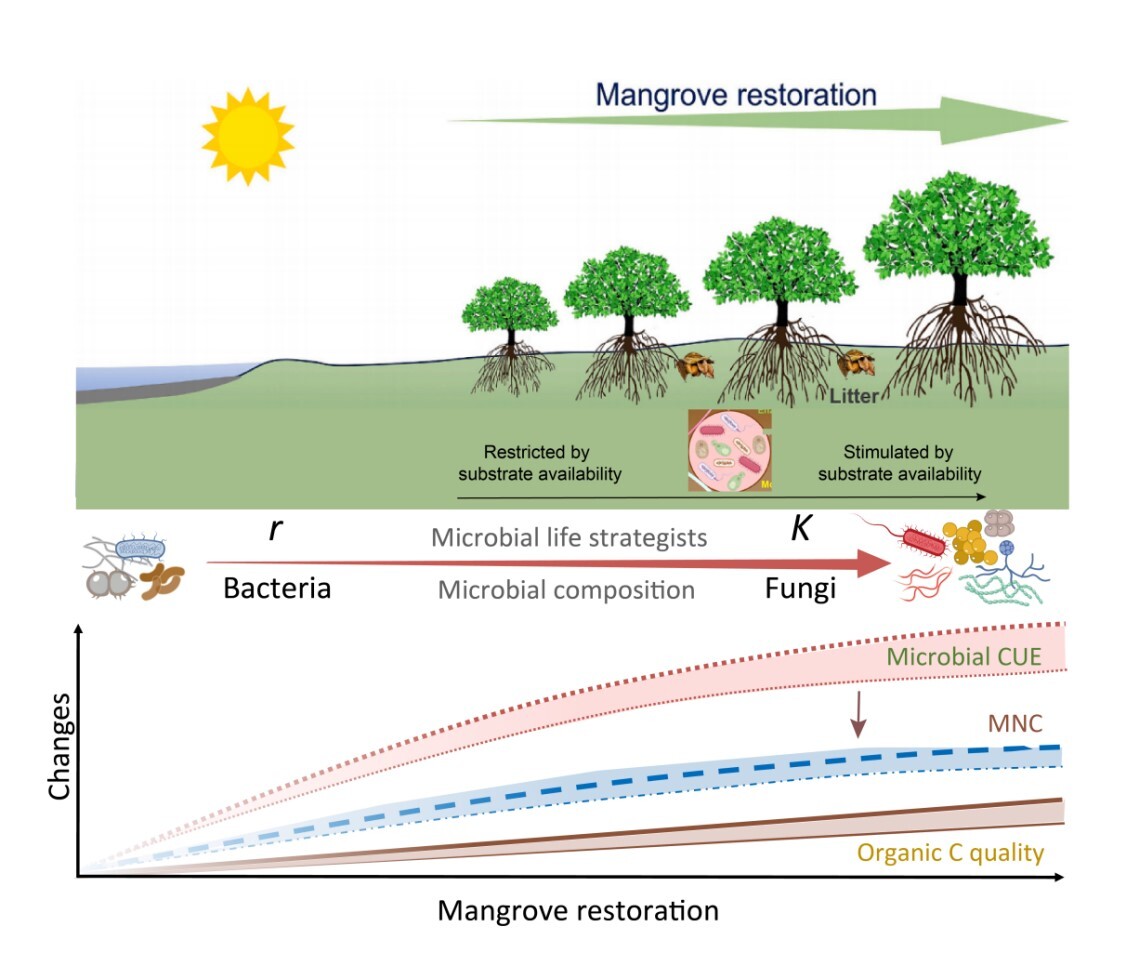
2026-01-29Scientific Breakthrough in Blue Carbon: Mangrove Restoration Enhances Soil Carbon Sequestration via Microbial PathwaysMangrove restoration significantly enhances microbial carbon use efficiency and promotes microbial necromass carbon accumulation by improving organic carbon quality and driving a shift in microbial community from r-strategists to K-strategists. These findings highlight the importance of incorporating microbial processes into restoration strategi... A recent study led by researchers (Prof. WANG Faming, Dr. HUANG Xingyun, and so on) at the Xiaoliang Experimental Station has shed new light on the crucial role of soil microbes in carbon sequestration during mangrove restoration, providing a novel microbial-driven perspective for enhancing "Blue Carbon" sinks.Published in the Journal of Plant E...Read More
-
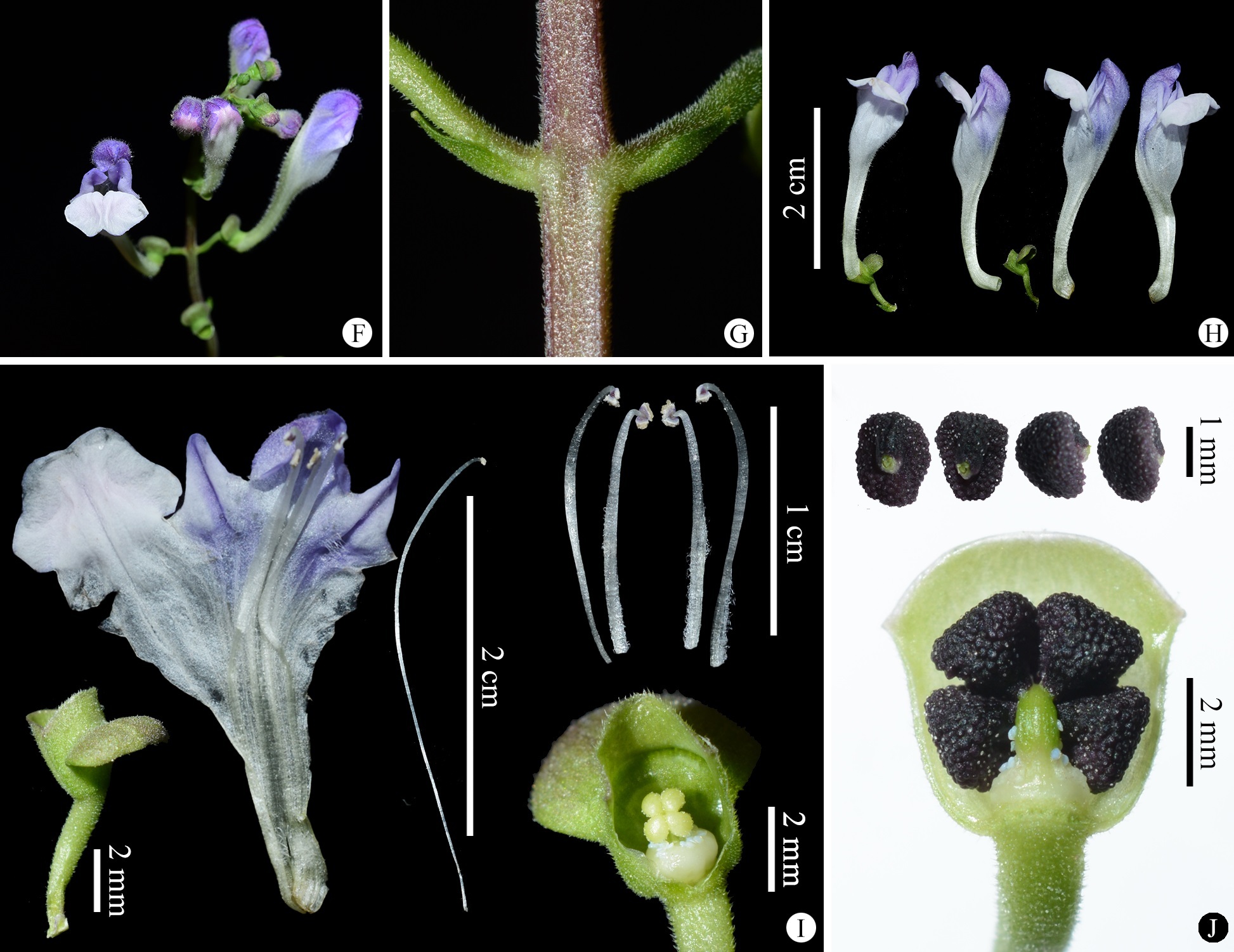
2026-01-29Unraveling the Taxonomic History of Scutellaria formosana: A Hundred-Year QuestBased on critical examination of original description and herbarium specimens and careful observations of living plants in the wild, we demonstrated that the type locality of Scutellaria formosana of Lamiaceae (also known as the mint family) previously regarded as a native of Taiwan or Hainan provinces, China, is actually Hong Kong, and S. formo... In 1894, a flowering Scutellaria plant from the Veitch & Sons nursery was described by the British botanist N. E. Brown as a new species, Scutellaria formosana Brown (Fig. 1). It was characterized by having glabrous stems, ovate leaves nearly obtuse at the apex, broadly cuneate at the base, inconspicuously toothed at the margin, and glabrous on ...Read More
-
2026-01-20Decoding the Genome of Brainea insignis Reveals Insights into Fern Evolution and ConservationFerns are an ancient lineage of vascular plants, yet limited genomic resources constrain both evolutionary and conservation inference. Here, we generate a chromosome-level genome assembly for the endangered cycad fern Brainea insignis (8.62 Gb), the sole species in its genus within eupolypods II, and integrate comparative and population genomic... The persistence of rare plant species is not only a matter of individual species survival but also underpins the maintenance of ecosystem functions and the continuity of long evolutionary histories. For monotypic genera, population decline or extinction entails the erosion or complete loss of entire evolutionary lineages, resulting in irreversib...Read More
-
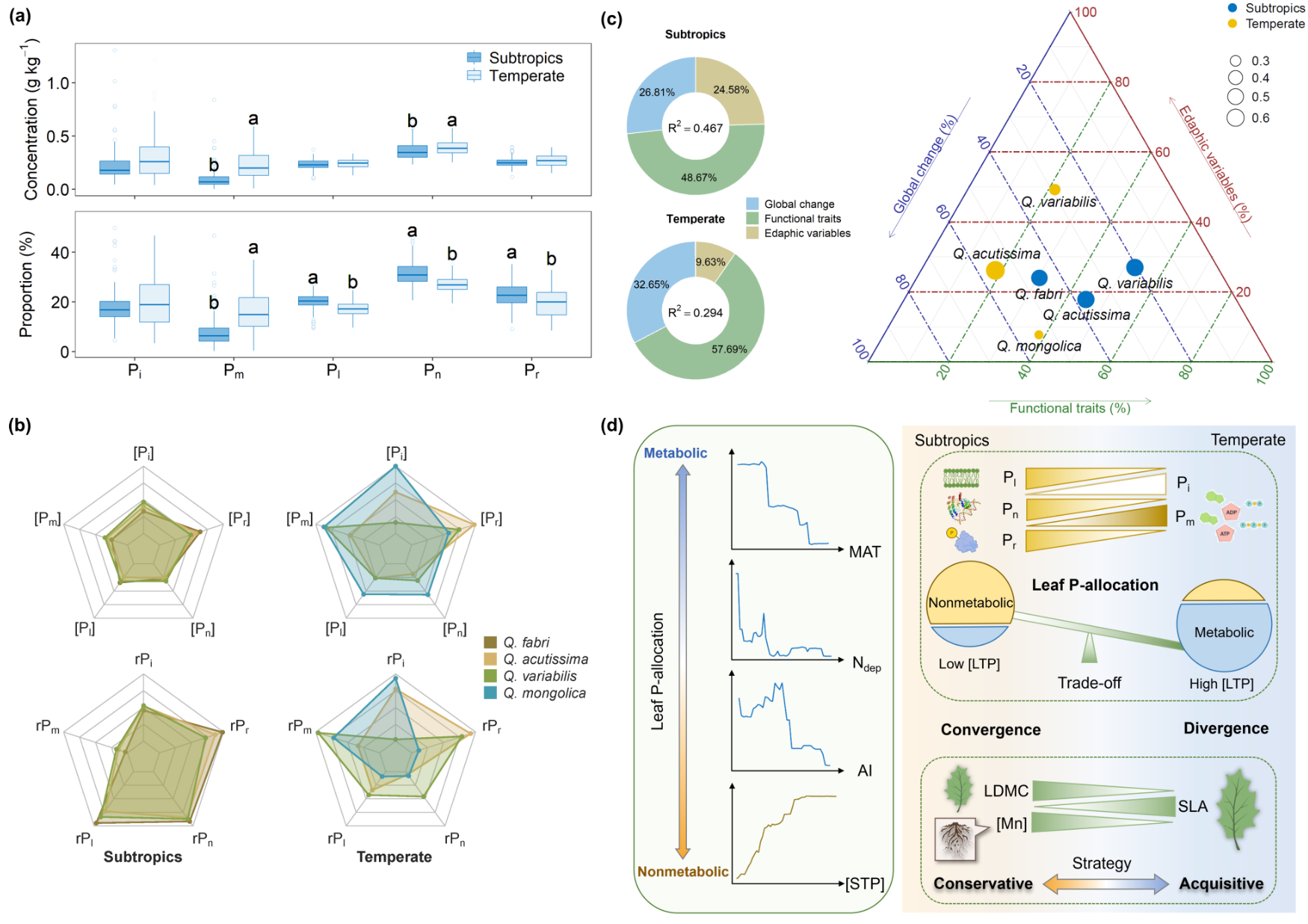
2026-01-09New progress on leaf phosphorus-allocation strategies of deciduous oaks in ChinaThis study unravels contrasting leaf P-allocation patterns of deciduous oaks in subtropical and temperate forests, which are mainly driven by global change rather than edaphic factors. It provides new avenues for exploring nutrient strategies of congeneric species growing in diverse environments. Allocation patterns of leaf phosphorus (P) reflect trade-off strategies of plants to maintain and/or enhance P-use efficiency under diverse environments. Understanding the variation in leaf P-allocation across geographic ranges is crucial for predicting the changes in plant growth and ecosystem functioning, and the potential geographic shifts of...Read More
-
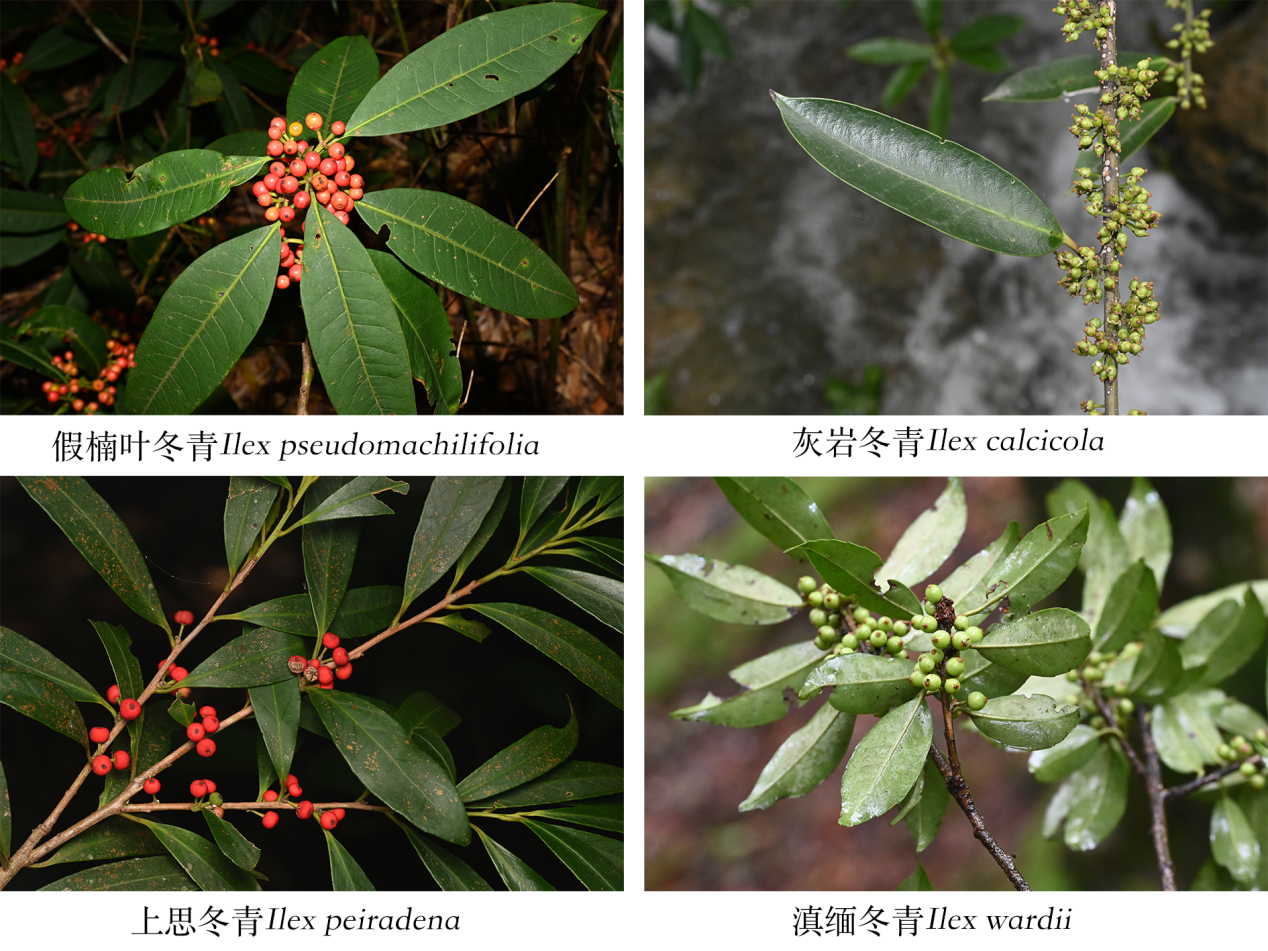
2026-01-07SCBG Completes Germplasm Collection of Ilex and Ancient TreeUnder the support of the National Wild Plant Germplasm Resource Center, researchers at the South China Botanical Garden completed two special collection works focused on Ilex and ancient trees. The efforts secured leaf materials and seeds, added first‑time species to the national holdings, and established genetic backups that extend conservatio... Recently, under the support of the National Wild Plant Germplasm Resource Center (the "National Center"), researchers at the Wild Plant Germplasm Resource Bank of the South China Botanical Garden (SCBG), Chinese Academy of Sciences, completed two special germplasm resource collection works focused on the Ilex and ancient trees.1. Ilex Germplasm ...Read More
-
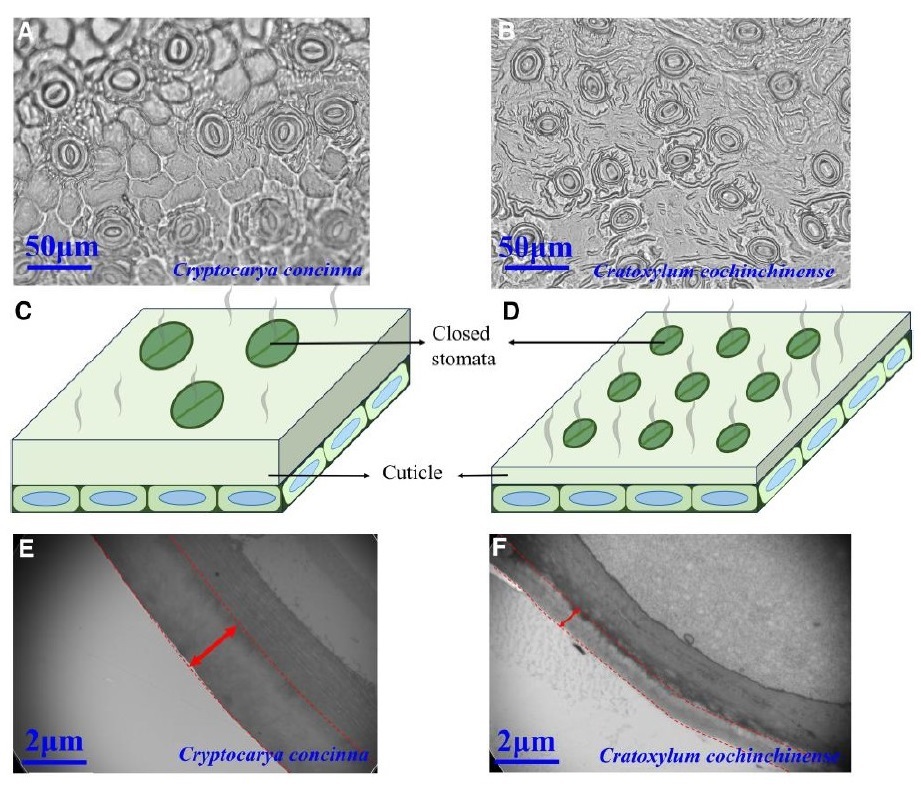
2026-01-01Restoration Ecology Research Team Reveals Interspecific Variation in Minimum Leaf Conductance Among Dominant Woody Species in Subtropical Forests and Its Key DriversThe cuticle determines minimum leaf conductance, with light requirement strategies driving species differences in cuticle thickness. Global climate change has profoundly altered terrestrial plant water relations. In particular, shifts in precipitation regimes, rising temperatures, and increasingly frequent extreme drought events pose serious challenges to plant growth and survival. Minimum leaf conductance (gmin) characterizes the rate of water loss after stomatal closure and...Read More