News
-
2019-01-14China has made progress in implementing Global Strategy for Plant Conservation(2011-2020)Plants are essential resources for the earth , and human survival .There are more than 380000 vascular plant species in the world and approximately 31150 in China . Many plant species are threatened with extinction because of the environmental consequences of a growing human population , urbanization and climate change .The Global Strategy for P... Plants are essential resources for the earth, and human survival. Many plant species are threatened due to human disturbance and global change. There are more than 380,000 vascular plant species in the world and approximately 31,150 in China. Many plant species are threatened with extinction because of the environmental consequences of a growing...Read More
-
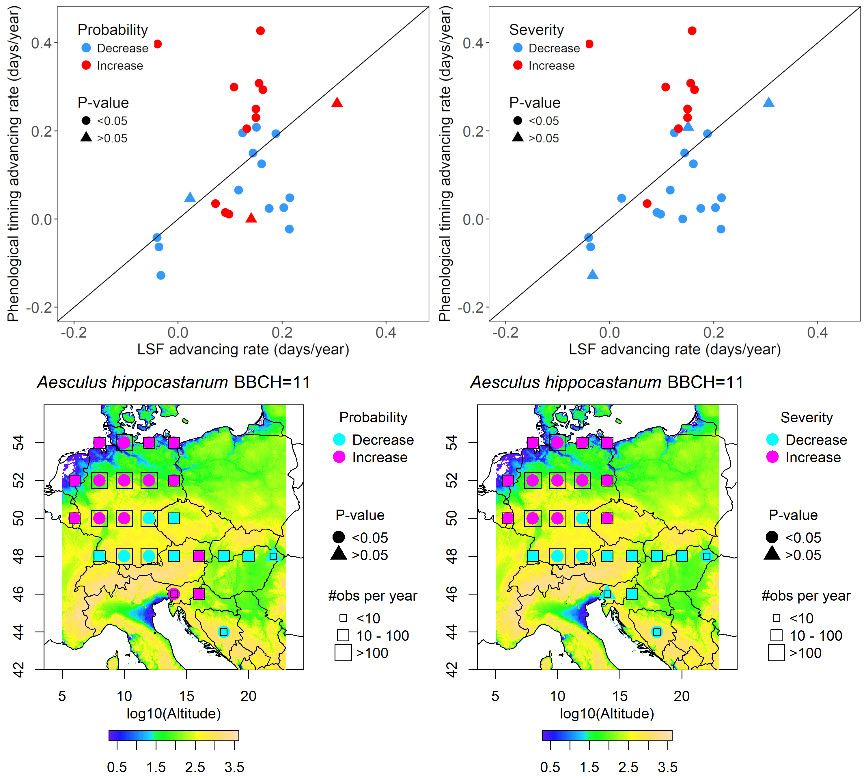
2019-01-03Divergent trends in the risk of spring frost damage to trees in Europe with recent warmingFrost events during the active growth period of plants can cause extensive frost damage with tremendous economic losses and dramatic ecological consequences .On the other hand , it has been argued that rising temperature in late winter and early spring might trigger the so called “ false spring ” , i . e . , early onset of growth that is follo... Frost events during the active growth period of plants can cause extensive frost damage with tremendous economic losses and dramatic ecological consequences. Cannell (1985) hypothesized, that climate warming in boreal and temperate zones increases the risk of frost damage to trees. This hypothesis has been addressed in several studies with model...Read More
-
2018-12-24The last exhibition of LIAN Natural Paintings held in South China Botanical GardenThe Natural Artwork Show " Beautiful China , LIAN Nature " , aims to present the beauty of China in the form of ecological paintings , reveal the vitality of the ecology with the brush of paintings .And awaken people ' s yearning for the beauty of nature .The exhibition started from the Beijing Botanical Garden and was held in 13 provincial and ... The Natural Artwork Show "Beautiful China, LIAN Nature",aims to present the beauty of China in the form of ecological paintings, reveal the vitality of the ecology with the brush of paintings, and awaken people's yearning for the beauty of nature. The exhibition started from the Beijing Botanical Garden and was held in 13 provincial and municipa...Read More
-
2018-12-07Beautiful Galsang Flower from Plateau--Western Student Exploration CampIn November 2018 , SCBG welcomed a group of special guests : 46 children from Galsang Flower Western Student Exploration Camp , Zaduo County , Yushu , Qinghai Province . They dressed in bright-colored Tibetan costumes .Just as beautiful as the Galsang flowers blooming on the plateau .On the lawn , teachers led children to play interesting Evol... In November 2018,SCBG welcomed a group of special guests: 46 children from Galsang Flower Western Student Exploration Camp, Zaduo County, Yushu, Qinghai Province. They dressed in bright-colored Tibetan costumes, just as beautiful as the Galsang flowers blooming on the plateau.Read More
Fig.1 The children took a group photo in front of the Conservato... -
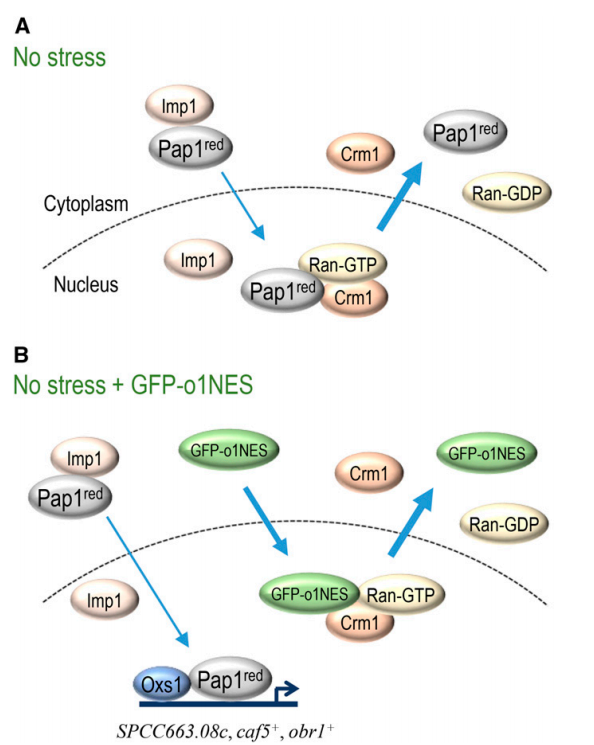
2018-12-07Protection from disulfide stress by inhibition of Pap1 nuclear export in fission yeastThe protection method of blocking Crm1 mediated export of nuclear proteins unraveled in this study may find medical relevance as an alternative to chemical drugs currently being tested to block the nuclear export of tumor suppressors in cancer therapy .The relevant paper entitled “ Protection from Disulfide Stress by Inhibition of Pap1 Nuclear ... Previous work from Dr. David W. Ow’s lab elucidated a new Pap1-Oxs1 pathway specific for the diamide-induced disulfide stress response in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, which appears to be evolutionarily conserved (He et al. 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 45: 106–114). In current study, PhD student Yan Chen and colleagues found that ov...Read More
-
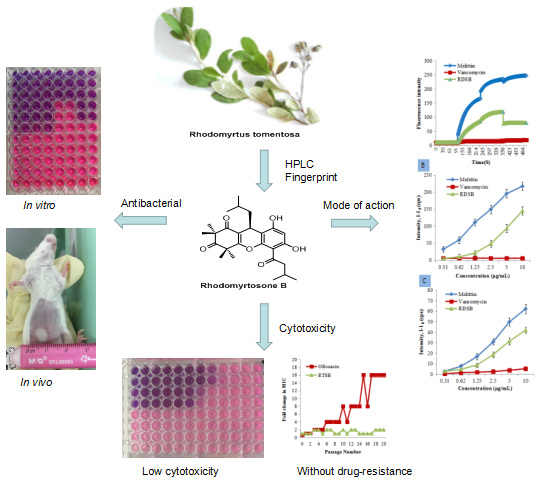
2018-11-26Medicinal chemistry of natural products rhodomyrtosone B against drug-resistant bacteriaRhodomyrtus tomentosa ( Aiton ) Hassk . , also named as Rose myrtle , is distributed in the hilly areas of Taiwan , Fujian , Guangdong , Guangxi , and Lingnan region .R . tomentosa is a medicinal and ornamental plant , and its sweet fruit is edible .The leaves of R . tomentosa are traditionally used in the treatment of infectious diseases such a... Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Aiton) Hassk., also named as Rose myrtle, is distributed in the hilly areas of Taiwan, Fujian, Guangdong, Guangxi, and Lingnan region. R. tomentosa is a medicinal and ornamental plant, and its sweet fruit is edible. The leaves of R. tomentosa are traditionally used in the treatment of infectious diseases such as wound infe...Read More
-
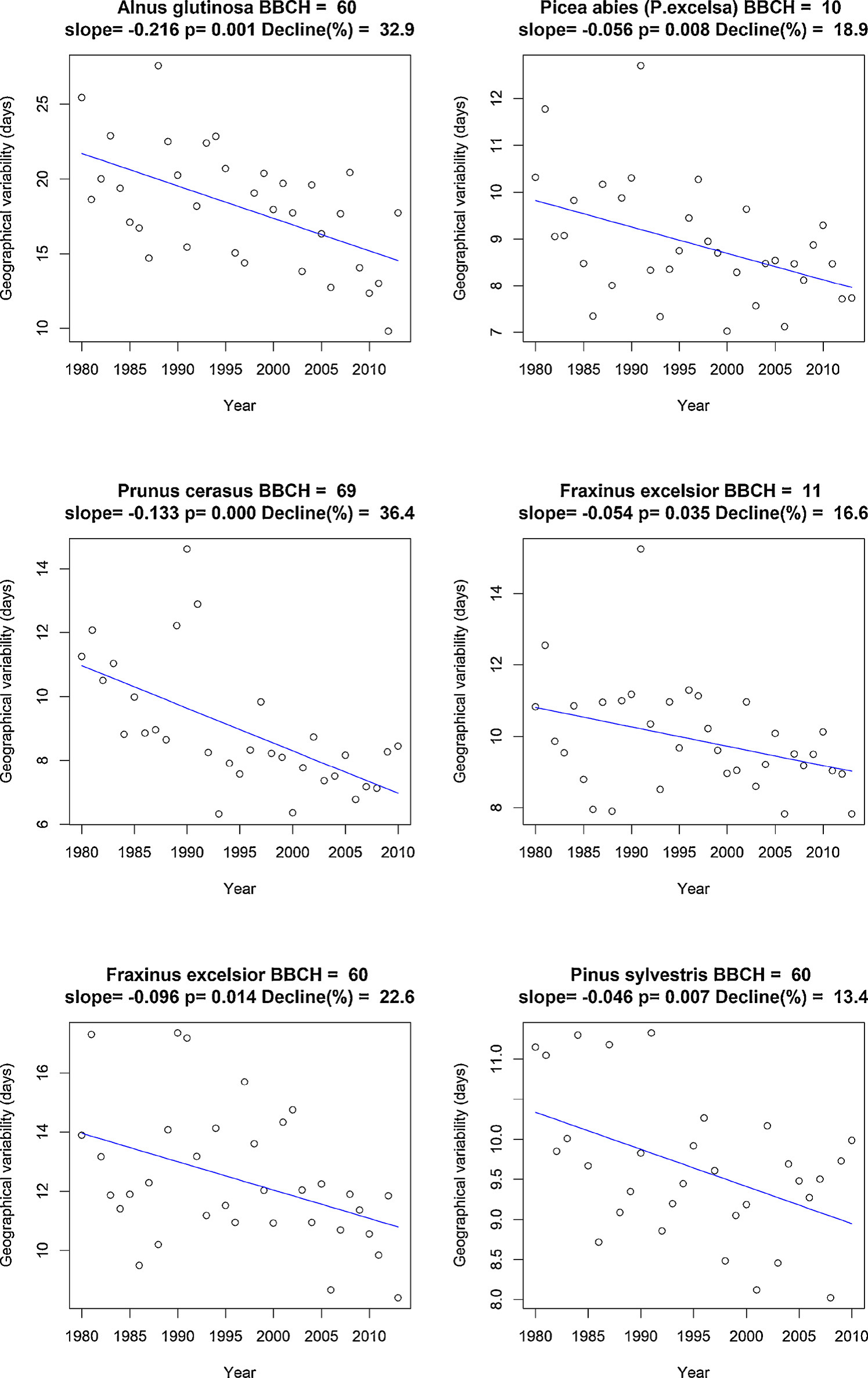
2018-11-21Reduced geographical variability in spring phenology of temperate trees with recent warmingAdvancements of spring phenology due to climate warming have been observed worldwide in the last decades , however .We addressed this question through analyzing temporal changes in the geographical variability for 22 spring phenological events ( both leaf-out and flowering phenology ) of 16 temperate tree species in Europe . This study , for the... Advancements of spring phenology due to climate warming have been observed worldwide in the last decades, however, whether the occurrence of species-specific phenology events among populations over broad space has been converged or diverged with recent warming has been little explored. We addressed this question through analyzing temporal change...Read More
-
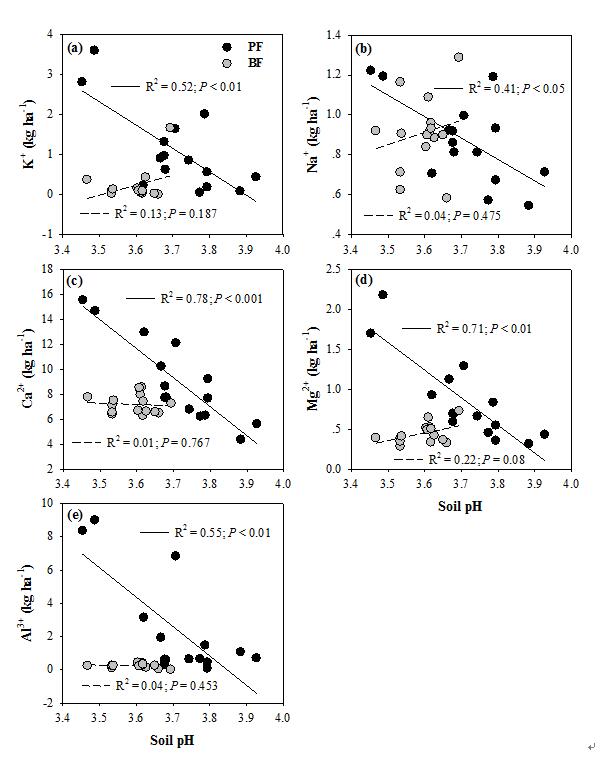
2018-11-05Mechanisms of acid buffering in acidic forest soils in southern ChinaElevated anthropogenic acid deposition has accelerated forest soil acidification in southern China . However , the observed responses to increased acid inputs are quite variable among different forest soils .Long-term observation data showed that the pH of an old evergreen broadleaved forest ( BF ) soils maintained around 3.8 under high rate of ... Elevated anthropogenic acid deposition has accelerated forest soil acidification in southern China. However, the observed responses to increased acid inputs are quite variable among different forest soils. Long-term observation data showed that the pH of an old evergreen broadleaved forest (BF) soils maintained around 3.8 under high rate of acid...Read More